When an acid reacts with a metal, it starts to bubble. This is because a gas called hydrogen is being made. At the same time, a kind of salt is formed and stays in the liquid.
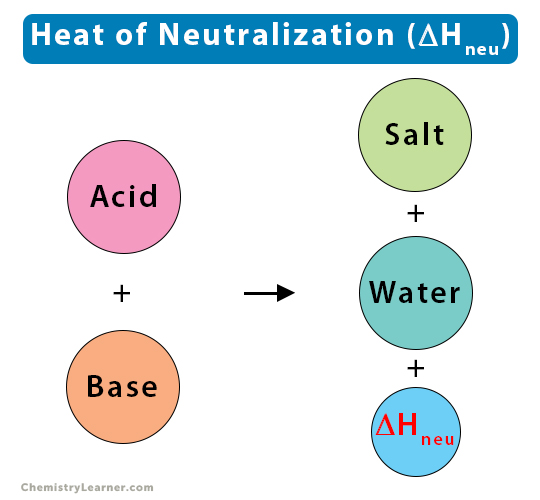
If you mix an acid with a base, they cancel each other out. This is called neutralization. The result is just water and salt, and the mixture becomes neutral — not too acidic or too basic.
When an acid touches a carbonate (like chalk or baking soda), it fizzes a lot. That fizz is carbon dioxide gas escaping. Along with the gas, water and a salt are also formed.
A metal oxide is a substance that acts like a base. When it reacts with an acid, it also neutralizes it. This makes water and a salt, but no gas is released.
A metal hydroxide works in the same way — it neutralizes the acid to make water and salt. It’s just a different type of base.