Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter part is an exhaust emission control device which converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas
Toxic gases produced from combustion that is caused from converting fuel energy to kinetic energy, the toxic gases produced during this process needs to be stopped
Catalyst is a substance that causes a chemical reaction to occur quickly
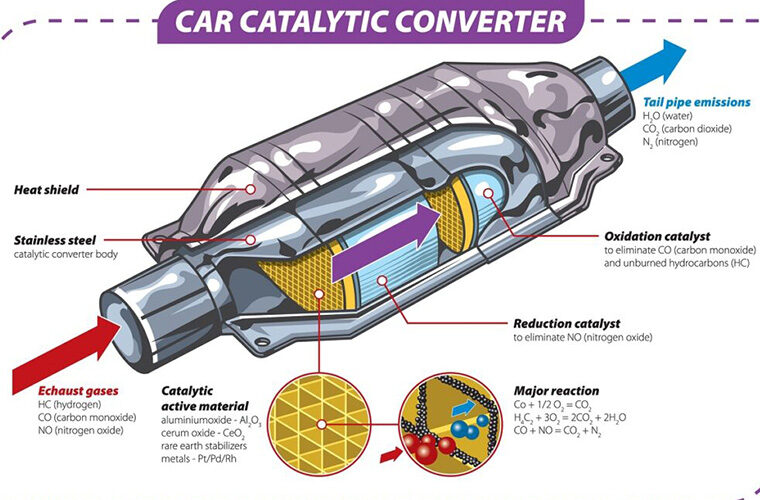
Exhaust gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide or nitrogen oxide are produced, The catalytic material takes in such gases and a reaction occurs
There are 2 types of catalyst in the following figure, a reduction and an oxidation catalyst
The purpose of oxidation and reduction is to stabilise such toxic compounds and make them safer and less toxic
This process makes such substances less toxic by catalytic converters utilizing redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions to detoxify exhaust gases. This process involves converting harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen
In the first process the substances are reduced before oxidised, this is because a substance cant lose electrons before gaining them, this is to fasten a reaction







How does the efficiency of a catalytic converter change over time?
What happens if a vehicle runs without a catalytic converter?
Can catalytic converters work in cold weather, or do they need a certain temperature to function properly?
How do catalytic converters help in reducing the environmental impact of fossil fuel use?
Why are catalytic converters often targeted for theft?
How is the performance of a catalytic converter monitored in modern vehicles?
Could catalytic converter technology be applied outside of automobiles (e.g., in factories or power plants)?
keywords
Emission
Catalyst
Platinum
Palladium
Rhodium
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ)
Hydrocarbons (HC)
Oxidation
Reduction